 Have you noticed the increasing contamination in the air we breathe? It’s not a surprise or a coincidence more and more people are developing allergies and other complications. Are air purifiers really a safe solution to this growing problem?
Have you noticed the increasing contamination in the air we breathe? It’s not a surprise or a coincidence more and more people are developing allergies and other complications. Are air purifiers really a safe solution to this growing problem?
Over 50 million Americans currently suffer from allergies and asthma. More and more people are becoming concerned about indoor air safety and quality. As a result, air purifiers are becoming a more popular feature in the home. When you select and use your air purifier correctly you will experience numerous benefits. This is especially true for people with allergies, asthma, or other breathing difficulties Even smokers, pet owners, and those who live with high pollution will benefit.
However, there are many factors to look into to ensure that the air purifier you purchase will do more good than harm. For example, there are many types to choose from, including HEPA filters, ozone generators, and air ionizers. In this article, you’ll find out everything you need to know about the most common types of domestic air purifiers, including how they work, potential side effects, and the pros and cons.
What are HEPA air purifiers?
HEPA air filters have been around much longer than you may think. Around 200 years ago, they were first used in the form of a fireman’s protective face mask. Since then, they have evolved for domestic use in the form of appliances known as HEPA air purifiers. They remove pollutants from the air through a filter and provide health benefits as a result. So how do they work, and what are their pros and cons?
How HEPA Works
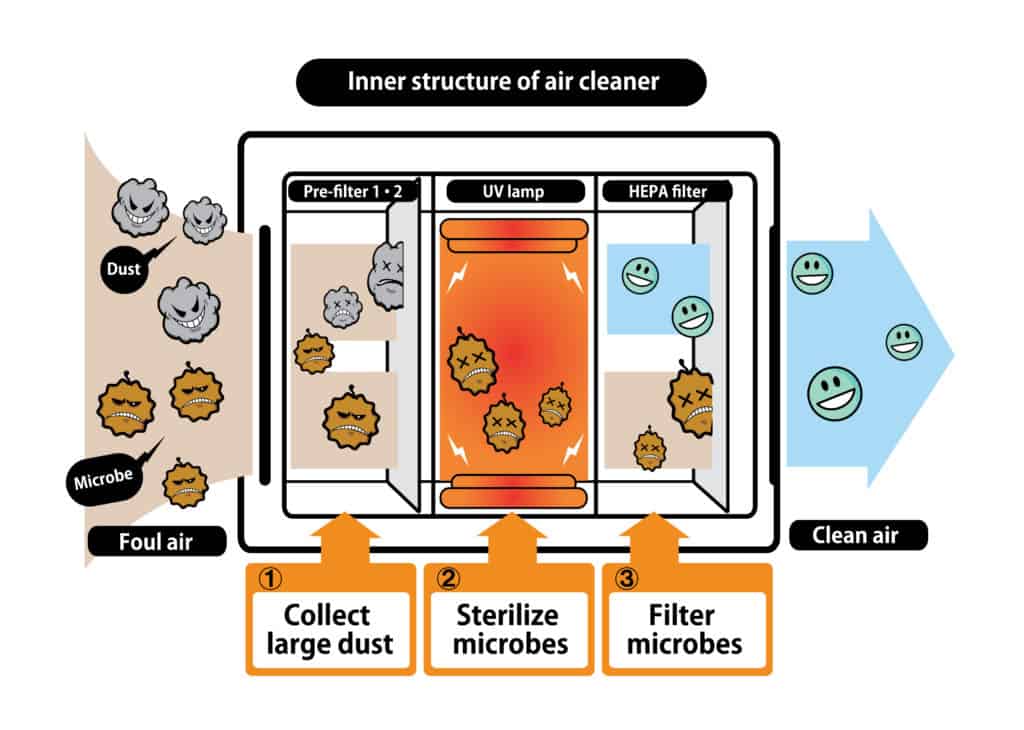
In the most simple terms, HEPA air purifiers attract air through a layered filter, capturing fine particles like dust and pollen before the air re-enters the space. Let’s get into a little more detail.
HEPA stands for high-efficiency particulate air and is an accepted benchmark for air filters. This type of air filter captures 99.97% of airborne particles smaller than 0.3 microns, where a micron is the standard unit for measuring air particles. For reference, the naked human eye cannot see particles below 10 microns in size.
They’re so good at trapping tiny particles it makes you wonder what they are made of? Without getting too scientific, HEPA filters are made of a mat of randomly arranged fibers. The fibers are usually fiberglass and are very thin with diameters between 0.5 and 2 micrometers. But rather than trapping unwanted particles in a sieve-like mechanism, these fibers trap particles in trickier ways, like forcing them to embed or stick to the fibers.
Pros:
- They last two to three years in residential settings
- Made to a standard recognized by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
- HEPA filters pose a low risk of pulmonary side effects due to mechanical design (rather than negative ions or ozone, for example)
Cons:
- HEPA air filters do not eliminate gases or odors. Chemical vapors, cigarette smell, or pet odors require the use of an activated carbon (charcoal) filter instead (or in addition)
- If replacement is left too late, they become ineffective
- Similar but less efficient filters are sold as “HEPA-type” or “HEPA-like”, so look out for “true” or “absolute” HEPA labels
What are air ionizers?
Unlike HEPA filters, air ionizers rely on chemical properties. Ionizing air purifiers give airborne particles a charge, forcing them to stick to other particles. That is why they often use fans and filters in addition to the primary ionizing system. Let’s get into the details.
How Air Ionizers Work
Also known as electrostatic precipitators, ionizing air purifiers use electricity to charge air atoms before discharging them into the space. They make regular air atoms collide with electrons, making them into negatively charged ions. They then release these in what is known as a corona discharge. A small electrical field forms as a result and airborne particles like dust and pollen enter it.
When airborne contaminants enter the electrical field, the ions attach to them and give them a negative charge. They will either attract positively charged particles, or the particles are attracted to charged metal plates within the purifier. Either that the particles become too large to remain airborne and settle, allowing for easy removal, or they are stick to metal plates in the system which is easy to clean.
The two major types of air ionizers are fan-based and fanless. While fan-based ionizing air purifiers are more effective at cleaning the air, fanless systems are much quieter and use less energy.
Pros:
- No replacements necessary
- Effective in removing pollutants down to 0.01 microns in size
- Excellent for people who live in large cities
Cons:
- Not the most effective at removing dust, pollen, dirt, and dander
- Ionizers produce trace amounts of ozone and other oxidants as by-products, although these are generally below the industrial safety standard of 0.05 ppm
What are ozone generators?
Ozone generators are the most controversial type of air purifiers, largely due to their potential risks and questionable effectiveness. As the name suggests, these systems produce ozone molecules, which manufacturers claim remove contaminants and odors from the air. However, ozone is toxic to humans. So how do they work, and what are the dangers?

How Ozone Generators Work
Ozone is a molecule comprised of three oxygen atoms, while most oxygen in the air is in the form of dioxygen or O2. Ozone generators expose dioxygen to a corona discharge (like the one created by ionizers) or UV light to split its atoms. Once the atoms split, some rearrange to form ozone gas.
Ozone is highly unstable and acts as a powerful oxidant. While this gives it some excellent applications, it also makes the gas extremely dangerous to organic tissues above 0.1ppm, and especially to mucous and respiratory organs. That is why it is most effective in high levels to sanitize and deodorize uninhabited enclosed spaces. Examples would be to remove air impurities and smells following a domestic fire or organic decay. It also sanitizes laundry, water, and food, but in these cases, people do not expose themselves to the gas itself.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has reported that at safe levels for people, ozone is not effective at eliminating contaminants, including odor, viruses, or bacteria.
Pros:
- Ozone has very strong oxidising properties, making it very effective for decontaminating water, textiles, and even food in commercial and industrial settings
Cons:
- Ozone is very damaging to organic tissues even in low concentrations and can lead to irritation and even injury to the eyes and respiratory organs including lungs
- Commercially sold ozone-generating air purifiers must maintain a safe level of ozone, making them largely (if not completely) ineffective
Hazardous Hoax or Risk-Free Respiration?
We’ve looked at the most common types of commercially available domestic air purifiers. We’ve covered how each one works, and what its pros and cons are. So are they worthwhile? Let’s compare.
HEPA filters are the safest of the three and tackle most airborne particles that can affect those with asthma or allergies. However, they do not remove odors from your home, so they are more effective in conjunction with a charcoal filter. A lot of models come with an activated carbon filter already built in.
Air ionizers are very effective and low-maintenance but produce trace amounts of ozone and other oxidants. Luckily, these are no cause for concern, as long as the product manufacturer meets regulations. Their biggest downside is the need to regularly clean the collection plate inside the system.
As for ozone generators, well, unless you have an industrial air purifying job coming up at an uninhabited location, it seems like it’s not worth bothering with these. Not only is ozone very hazardous to human respiratory tissues, but the commercially available ozone generators don’t produce nearly enough of the gas to actually make a difference to air quality. Save your money and buy something safe that actually works!

